BRCA1 and BRCA2
BRCA1 (BReast CAncer gene 1) and BRCA2 (BReast CAncer gene 2) are so-called tumour suppressor genes whose proteins, for which they code, are also responsible for DNA repair.
In addition to spontaneous mutations of the BRCA genes, one of the two gene copies may already be mutated, having been passed on by a parent. The heterozygous presence of a BRCA mutation increases the risk of ovarian cancer and breast cancer (BRCA1 ~5x, BRCA2 ~ 8x). BRCA Gene Mutations: Cancer Risk and Genetic Testing
Own studies for radiation sensitivity:
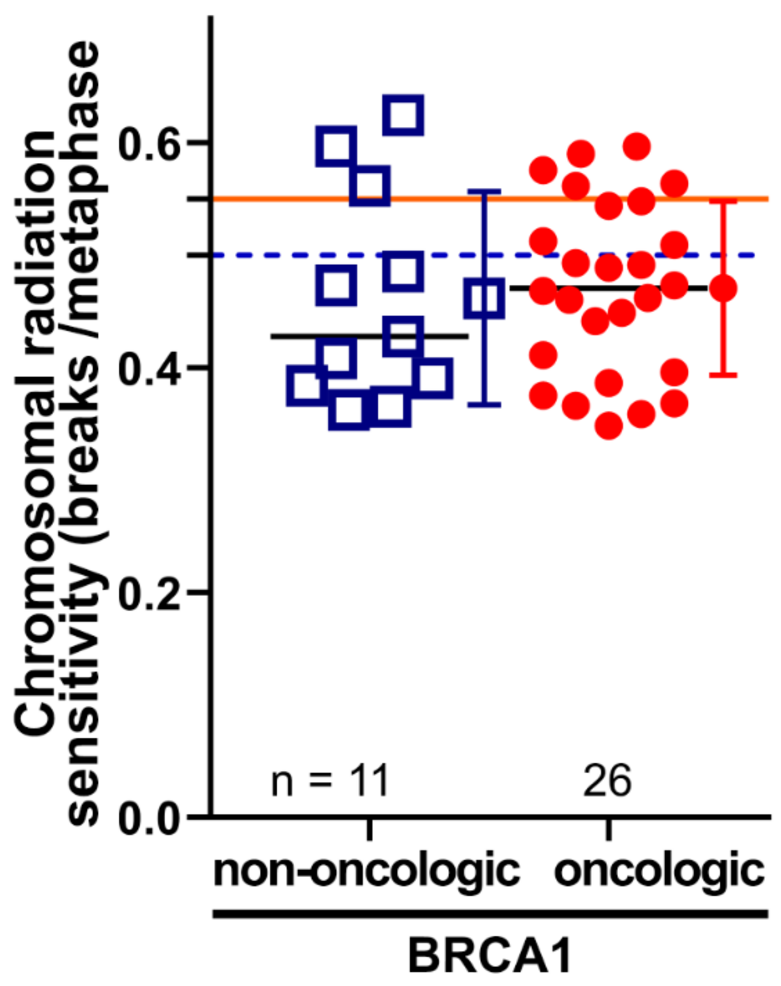
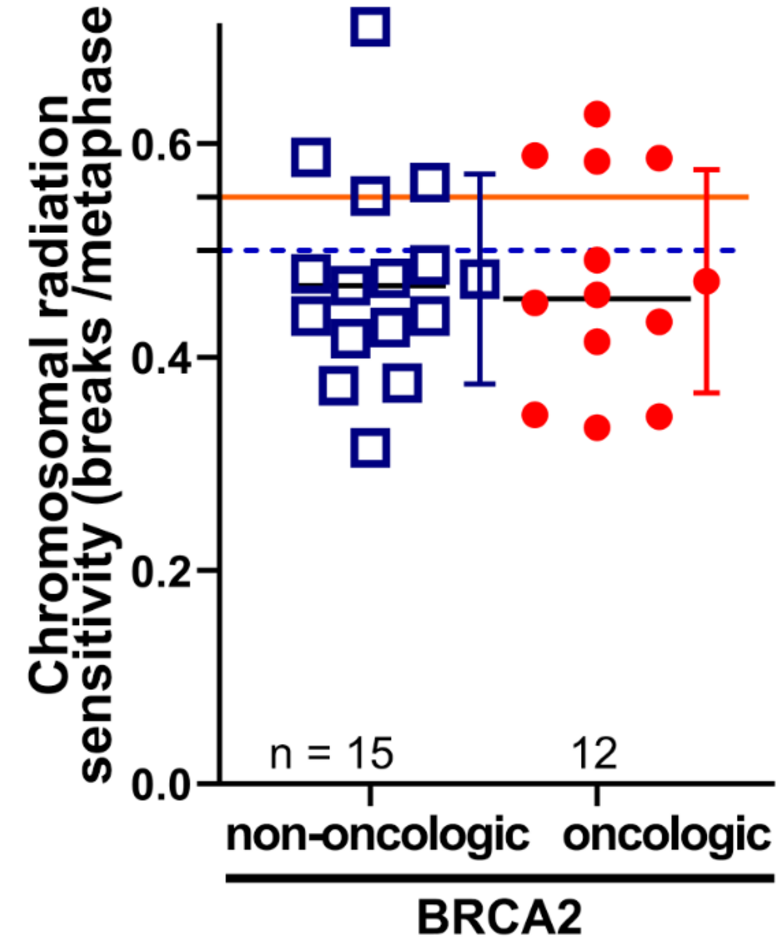
- 64 breast cancer patients with a known BRCA1 or 2 mutation were studied.
- 37 patients with BRCA1 mutations had not or only slightly increased radiation sensitivity in our studies.
- 27 patients with BRCA2 mutations had not or only slightly increased radiation sensitivity in our studies.
- One patient with BRCA1 mutation and simultaneous Xeroderma pigmentosum and Bloom's Syndrom had significantly increased radiation sensitivity.
- One patient with BRCA1 and CHEK2 mutation had no increased radiation sensitivity with 0.46 B/M
- A patient with BRCA2 and Li Fraumeni syndrome (p53 het.) had an clearly increased radiation sensitivity of 0.6 B/M

![[Translate to English:] Strahlenempfindlichkeit von Patientinnen mit BRCA1 oder BRCA2 Mutationen [Translate to English:] Strahlenempfindlichkeit von Patientinnen mit BRCA1 oder BRCA2 Mutationen](/fileadmin/_processed_/c/0/csm_BRCA1_2_B_M_7cff724f59.png)