About the Project:
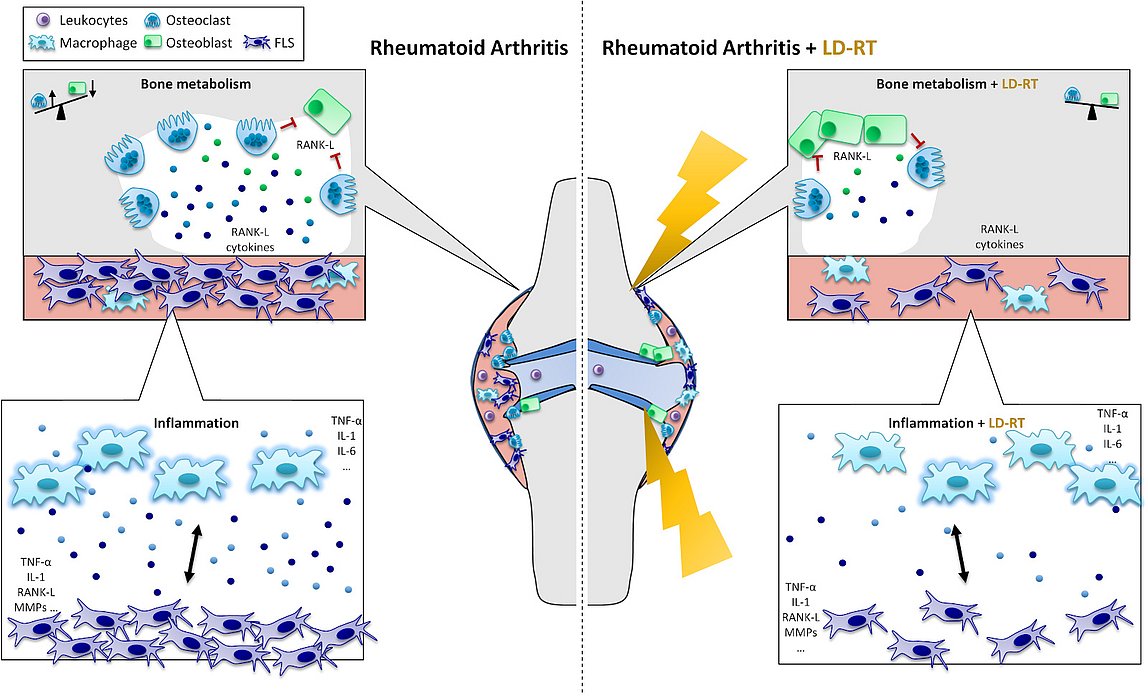
One of the best-known beneficial effects of a therapy with low doses of ionizing radiation (low-dose radiotherapy, LD-RT) as patients report them, are the often long lasting analgesic effects. While little is known about the exact underlying mechanisms for this effect, research generally suggests a wide range of LD-RT induced modifications. Among the best-studied biological effects are the anti-inflammatory properties of LD-RT. However, there is also evidence, that LD-RT positively influences bone growth and within the GREWIS project (GREWIS, 02NUK017G and GREWIS-alpha, 02NUK050E), we revealed, that, besides of the anti-inflammatory effects, LD-RT also possesses bone-protective effects in a model system for rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
In this project we are mainly focusing on bone cells (osteoclasts and osteoblasts), as well as on macrophages and fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS). All of these cells are involved in the initiation and upkeep of inflammation and direct or indirect destruction of joints in RA. These cell types are looked into either alone or in interplay with each other to further elucidate the base mechanisms behind the observed bone-protective effects of LD-RT.
We utilize primary cell cultures of inflammatory-primed or healthy origin as well as other preclinical model systems to examine the complex interplay of the immune and the bone system after a X-ray therapy at the Radiation Oncology in Erlangen and after a radon inhalation therapy in cooperation with the Gesellschaft für Schwerionenforschung (GSI) in Darmstadt, as a second example for an additive therapy for inflammatory, degenerative diseases of the musculoskeletal system. By closely mimicking the set-ups used in patient treatment and interaction with the clinic, we aim to not only gain a better understanding of the mechanisms but also to transfer the obtained knowledge in our patient studies as well as into the clinical routine. Further, the gained knowledge about osteoimmunological effect of low doses paves the basis for consecutive analyses and recommendations for radiation protection issues.
Team
Methods:
Multicolor Flow Cytometry, (Endpoint) PCR, Quantitative PCR, ELISA, Primary Cell Cultures, Preclinical Model Systems, Histology, Histomorphometry, MSD System (Multi-Array Technology), Low-Dose Radiotherapy (X-rays), Radon Chamber (at GSI), Standard Molecular Techniques, Microscopic Analysis
Selected Publications
Radon Improves Clinical Response in an Animal Model of Rheumatoid Arthritis Accompanied by Increased Numbers of Peripheral Blood B Cells and Interleukin-5 Concentration. Deloch L, Hehlgans S, Rückert M, Maier A, Hinrichs A, Flohr AS, Eckert D, Weissmann T, Seeling M, Nimmerjahn F, Fietkau R, Rödel F, Fournier C, Frey B, Gaipl US. Cells 16;11(4):689 (2022)
Low-Dose Radiotherapy Leads to a Systemic Anti-Inflammatory Shift in the Pre-Clinical K/BxN Serum Transfer Model and Reduces Osteoarthritic Pain in Patients. Weissmann T, Rückert M, Zhou JG, Seeling M, Lettmaier S, Donaubauer AJ, Nimmerjahn F, Ott OJ, Hecht M, Putz F, Fietkau R, Frey B, Gaipl US, Deloch L. Front Immunol. 3;12:777792 (2022)
Low-dose radiotherapy ameliorates advanced arthritis in hTNF‐α tg mice by triggering osteoimmunological mechanisms. L. Deloch, B. Frey, A. Derer, A.J. Hueber, M. Herrmann, J. Wölfelschneider, J. Hahn, P.F. Rühle, J. Fuchs, R. Fietkau, U.S. Gaipl Frontiers in Immunology; 9:1834 (2018)
